Interoperability of Mobile Money Providers
Context
You want to collect money from an MTN Money wallet and then, for example, transfer the money received to an Orange Money or Moov Money wallet.
In Details
Our engineers have enabled strict interoperability between the Mtn Money, Orange Money and Moov Money wallets. So you can receive money from a customer on Moov Money and pay a supplier via Orange Money or Mtn Money, for example.
The possible combinations are infinite, and there's no extra integration effort on your part: all you have to do is collect money wherever you want, then transfer it to the destination of your choice, with ease.
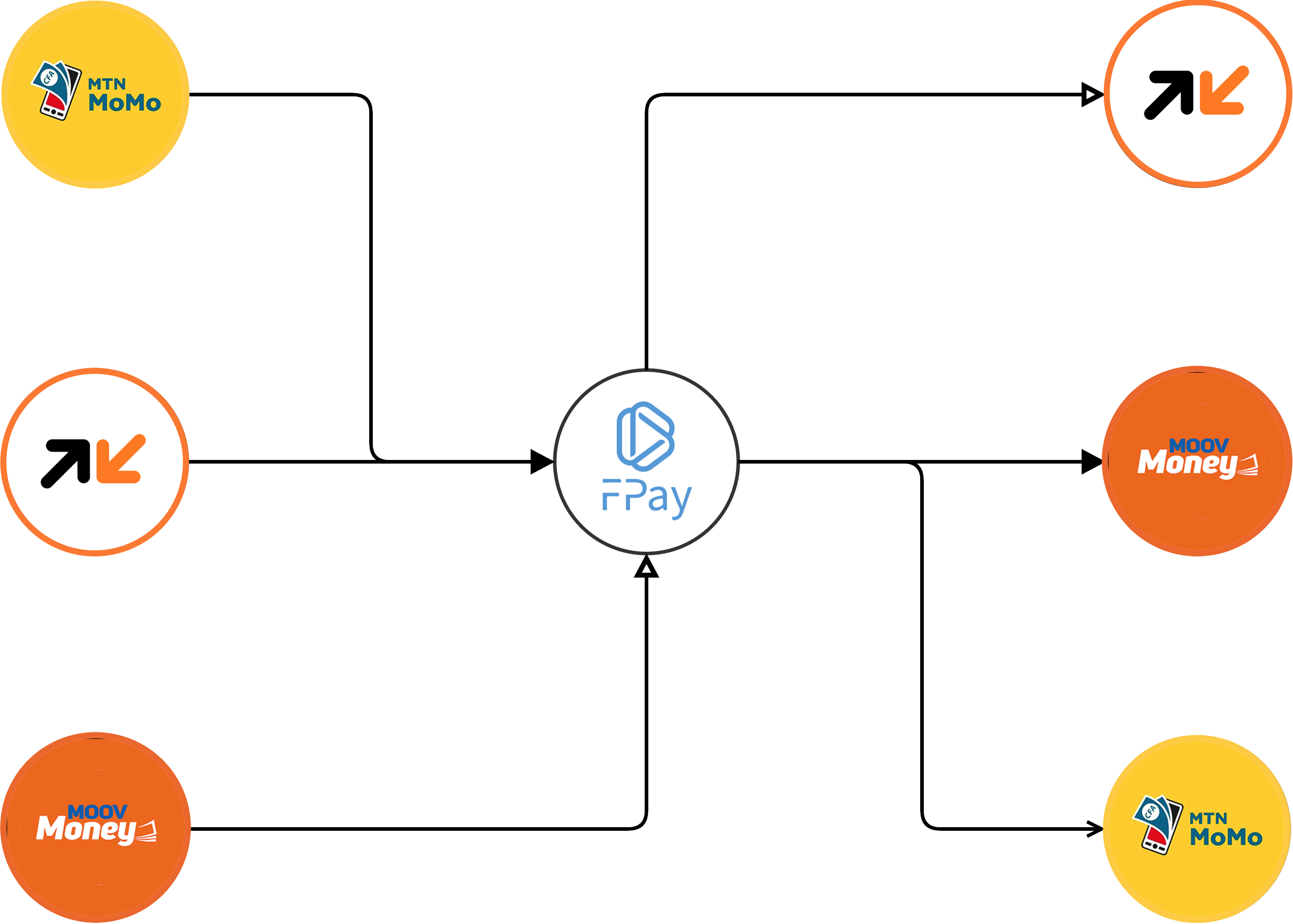
In the following section, we'll take a look at some code examples that show you how to interact and transfer money to and from different mobile money operators.
Pre Requisites
This SDK requires
Node >=9.5
Authentication
We assume that you have of course opened your FPay account and that you are in possession of your token and your secretKey obtained during the creation of the
AuthAccess object as explained on the Authentication page.Initialization
In
AuthAccess object, the value of the field named secretKey must be kept absolutely secret and used only on your servers. This implies that you should never use the value of this field as a variable or constant in the source code of a mobile application, a web application or in the source code of any application whose binary may be public and visible to all. There are many tools to access strings in the source code from a binary around here.const fPay = sdk.FPayClient(sdk.Auth({token: '<token>', secretKey: '<secretKey>' }));Receiving money
To receive money with FPay, we need to use either a Deposit object or aFundRequest object. The first object allows you to withdraw money directly from your user's account, while the second allows you to invite your users to choose to send you money from the mobile money provider of their choice.
For the rest of this example, we'll concentrate on the Deposit object, which assumes that we know in advance the provider with whom we wish to collect money.
Here are a few examples:
// Deposit from OrangeMoney sourceconst depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
},
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "07xxxxxxxx",
providerKey: "OrangeMoney"
}
},
h1: "Shopping cart payment #12"
});// Deposit from MtnMoney sourceconst depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
},
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "05xxxxxxxx",
providerKey: "MtnMoney"
}
},
h1: "Shopping cart payment #12"
});// Deposit from MoovMoney sourceconst depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
},
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "01xxxxxxxx",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
h1: "Shopping cart payment #12"
});Sending money
To send money with FPay, we need to use either a Transfer object or aQuasiTransfer object. The first object allows you to send money directly from your wallet to your user's account, while the second allows you to invite your users to choose to receive you money to the mobile money provider of their choice.
For the rest of this example, we'll concentrate on the Transfer object, which assumes that we know in advance the provider to which we wish to transfer money. transfer money.
Here are a few examples
// "Transfer to OrangeMoney destination"const transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
},
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "07xxxxxxxx",
providerKey: "OrangeMoney"
}
},
h1: "Shopping cart payment #12"
});// Transfer to MtnMoney destinationconst transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
},
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "05xxxxxxxx",
providerKey: "MtnMoney"
}
},
h1: "Shopping cart payment #12"
});// Transfer to MoovMoney destinationconst transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
},
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "01xxxxxxxx",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
h1: "Shopping cart payment #12"
});Going Further
Multi Language Support
When creating the Deposit and Transfer objects, if you specify the h1 field , the value entered will be displayed to your user as the reason for payment. It is possible to specify a value in English and a value in French.
How its works?
Deposit
const depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
h1: {
fr: "Paiement panier #12",
en: "Shopping cart payment #12"
},
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
}
});Transfer
const transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
h1: {
fr: "Paiement panier #12",
en: "Shopping cart payment #12"
},
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
}
});Source
Whenever you send money out of your account, the funds sent will be taken from your main Wallet by default. Because you can create several additional Wallet , you can also choose the source of the funds to be sent.
So, you can have one Wallet for your savings, or one Wallet per store if you have several stores, and choose where the funds to be transmitted will be taken from.
How it works ?
To specify the source of the funds, you need the MARS of the Wallet, available vie the mars.alpha field.
For example, if the Wallet's MARS is "CI FPay W09POT", then you would enter the following code:
const transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
source: "CI FPay W09POT",
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
}
});Destination
Whenever money is added to your account, the funds collected will be deposited in your main Wallet by default. Because you can create several additional Wallet , you can also choose where the funds arrives once the user has paid.
So, you can have one Wallet for your savings, or one Wallet per store if you have several stores, and choose where the funds received will go.
How it works ?
To specify the destination of the funds, you need the MARS of the Wallet, available vie the mars.alpha field.
For example, if the Wallet's MARS is "CI FPay W09POT", then you would enter the following code:
const depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
destination: "CI FPay W09POT",
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
}
});Fees Payer
By default, transactions fees are paid by your customer. You can specify specify who pays them to change this default behavior according to the situations you need to manage.
For example, suppose you want to make a cash inflow to your FPay account in the amount of ₣ 10,000 The question you need to ask yourself is How much money my user should pay ? If the answer is ₣ 10,000, then then you pay the fees.
You can also ask the question the other way around: How much money should arrive on my FPay account? If the answer is ₣ 10,000, then it's your user who will pay the fees.
To specify who pays the fees, 4 values are possible:
"Me"- You pay the fees
"CounterPart"- Your user (the counter part) pays the fees
"Sender"- Whoever sends the money pays the fees, whether it's you or your user
"Receiver"- Whoever receives the money pays the costs, whether it's you or your user.
Code example
Deposit
const depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
fees: {
payer: "CounterPart"
},
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
}
});Transfer
const transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
fees: {
payer: "CounterPart"
},
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
},
amount: {
currency: "XOF",
value: "10_000"
}
});Foreign ID
When creating the Deposit and Transfer objects, you can attach your own internal ID. In this way, When retrieving the Deposit and Transfer objects, you will be able to use your own id instead of the one generated by FPay. The ID you submit must be unique for each object type.
One of the advantages of submitting your own unique identifier is that you can carry outidempotent queries. In fact, if your submitted foreignId is unique, then you're protected against duplications due to networks, for example, and you'll be able to control retries without worrying about repeating the same operation several times.
For creation
Deposit
const depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
foreignId: "<my internal id>",
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
}
});Transfer
const transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
foreignId: "<my internal id>",
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
}
});At retrieval
With the previous code, you now have the right to do the following code to retrieve Deposit and Transfer objects.
Deposit
const depositPromise = fPay.deposit.get("<my internal id>");Transfer
const transferPromise = fPay.transfer.get("<my internal id>");Foreign Data
When creating Deposit and Transfer objects, you can add your own data to tag the object you've created.
For example, you can add the following data:
-
{"myKey": 19, "myOtherKey": "myOtherValue"} -
<xml><myKey>myValue</myKey></xml> -
myValue1, myValue2, myValue3 - Any string you like, as long as it doesn't exceed 255 characters.
On creation
Deposit
const depositPromise =
fPay.deposit.initiate({
foreignData: "<xml><myKey>myValue</myKey></xml>",
source: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
}
});Transfer
const transferPromise =
fPay.transfer.initiate({
foreignData: "<xml><myKey>myValue</myKey></xml>",
destination: {
_type: "Single",
account: {
country: "CI",
identifier: "+2250100000000",
providerKey: "MoovMoney"
}
}
});When retrieving
Deposit
const depositPromise = fPay.deposit.get("<deposit.id | foreignId>");depositPromise.then(deposit => {
// Inspect the 'foreignData' field of the Deposit ...
const xmlData = deposit.foreignData;
// xmlData = "<xml><myKey>myValue</myKey></xml>"
});Transfer
const transferPromise = fPay.transfer.get("<transfer.id | foreignId>");transferPromise.then(transfer => {
// Inspect the 'foreignData' field of the Transfer ...
const xmlData = transfer.foreignData;
// xmlData = "<xml><myKey>myValue</myKey></xml>"
}); Français
Français English
English